
Mushroom Spore Microscopy: Mushroom Spores for Microscopy
Spore Syringes for Microscopy – Mushroom Spore Microscopy Guidance
Qualityspores.store has mushroom spores for microscopy or spore syringes for microscopy for sale along with necessary equipment and guidance. Amateur microscopy spores examination is a wonderful area of study, even if it’s “just” as a hobby as is the study of microscopy technology advances in 2022. Few other hobbies have the following characteristics:
- Spores for microscopy is affordable to start studying as a hobby
- Practitioners develop real-world science skills with microscopy mushrooms studying
- A nearly endless source of subjects to study—just look in your back yard
- A must for beginner mycologists, taxonomists, and mushroom enthusiasts
- Educational opportunities running the gamut including but not limited to science, biology, anthropology, history, botany, and, of course, mycology
- Study the many different types of fungi mushrooms.
Study Cubensis Spores Using Quality Mushroom Spore Syringes
Excited yet? Study mushroom spores under microscope equipment. It gets better: here at Quality Spores, we only stock premium spores packaged in the highest quality mushroom spore syringes for microscopy and research purposes, along with the top spores microscope selections. If you’re at all interested in mushroom fungi, seeing them at their earliest stage of development is nothing short of breathtaking. It’s not an exaggeration to say that spores can be just as visually stunning as their mature counterparts, if not more so!
Mushroom Spores Microscope

In this Quality Spores resource, we’ll be covering everything you need to know to start your journey as a home scientist and amateur microscopist using a mushroom spores microscope. While we encourage you to use your microscope to study just about anything you can get your hands on – leaves, insect wings, minerals, and much more can be wonderful to look examing. We’ll be discussing things within the context of mushroom taxonomy and spore microscopy.
Find out about the budding field of ethnopharmacology, get a brief history lesson on ethnopharmacology and the past of psychoactive mushrooms history, and take a look into what the future may hold as researchers the world over continue to discover the many benefits of medicinal mushroom spores.
Regarding amateur spore microscopy. In this article, you’ll learn:
- Advice on purchasing a great microscope for at-home study
- Additional supplies you may need
- How to best view and study mushroom spores
- Which mushroom spores are most often recommended for beginner researchers
- Legal questions answered with information on how to buy mushroom spores online
If you already own a microscope and consider yourself an expert, you may skip the following three sections and begin reading “How to View and Study Mushroom Spores Under Your Microscope,” however, if you’re just starting out or could use a refresher on the basics of microscopy, please continue below:
How a Microscope Works: Basic Parts and Assembly
A microscope, at its core, is simply a visualization tool that allows the user to see tiny objects, such as cells, microstructures, and microorganisms. Microscopes often offer more than a single level of magnification for exploring cubensis microscopy, allowing the user to visualize a subject in different ways. Microscopes have been used by scientists since the 16th century, and only continue to become more precise and affordable.
The three primary components of a microscope to examine cubensis spores under microscope lab equipment are the head, the base, and the arm. The head is the “body” of the microscope (and is sometimes referred to as such in certain documents and instructions, so keep that in mind). The head is responsible for carrying optical components.
The base of the microscope is more than simply a support for the device. It also acts as a surface for specimens, usually placed on a slide, and has lights called microscopic illuminators to help the user see the subject.
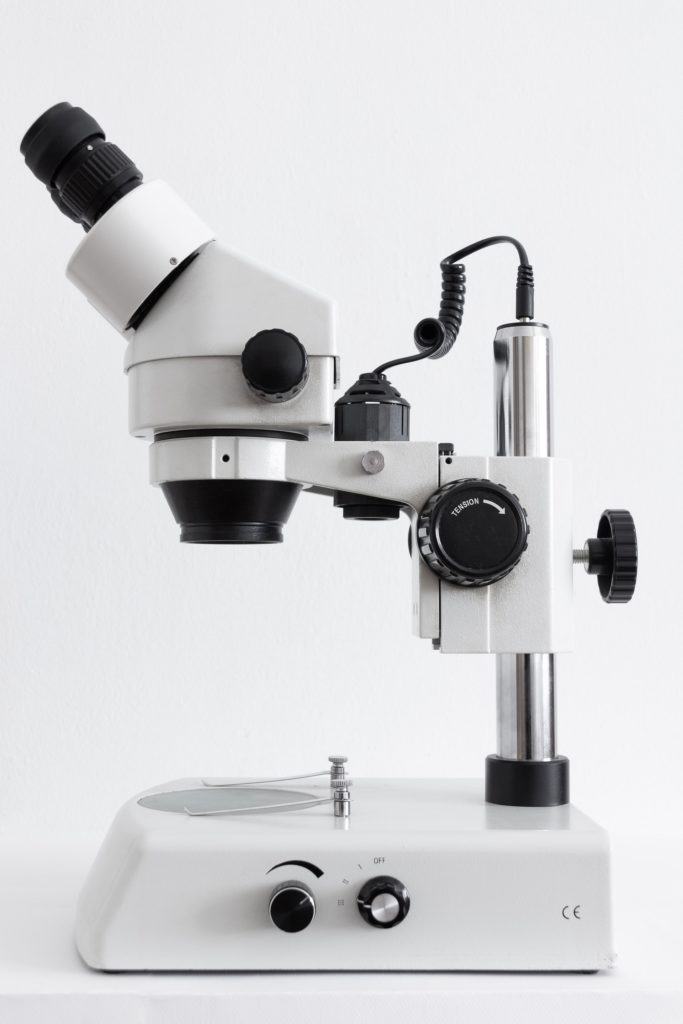

The arms of a mushroom spores microscope are easily recognizable – it’s the bit that connects the base to the head. Most microscopes are intended to be safely carried by the arm. Most microscopes have a stationary arm, but higher-end models may have jointed arms that allow the user to manipulate the position of the arm (and thus the head and viewing apparatus).
Perhaps the most important of all—at least the most interesting, anyway—are the optical components of the microscope. These components are where price will come into play as well, which we’ll learn more about in the following section. There are many optical components in a microscope to enable successful microscopic viewing, but we’ll touch on some of the primary ones now.
The eyepiece is, of course, where you look through the microscope. Some guides may refer to this as the “ocular” section of the microscope. Magnifications of the eyepiece alone usually range from 5 to 30 times magnification. Eyepieces can be binocular or monocular, which means that there are two or one viewing ports, respectively.
Next are the lenses, where the “real” magnification takes place. These lenses are often referred to as the major lenses, the objective lenses, or the primary lenses. They usually can reach magnification of somewhere in the range of 40 to 100 times. Most microscopes have between one and four major lenses, each with their own degree of magnification power.
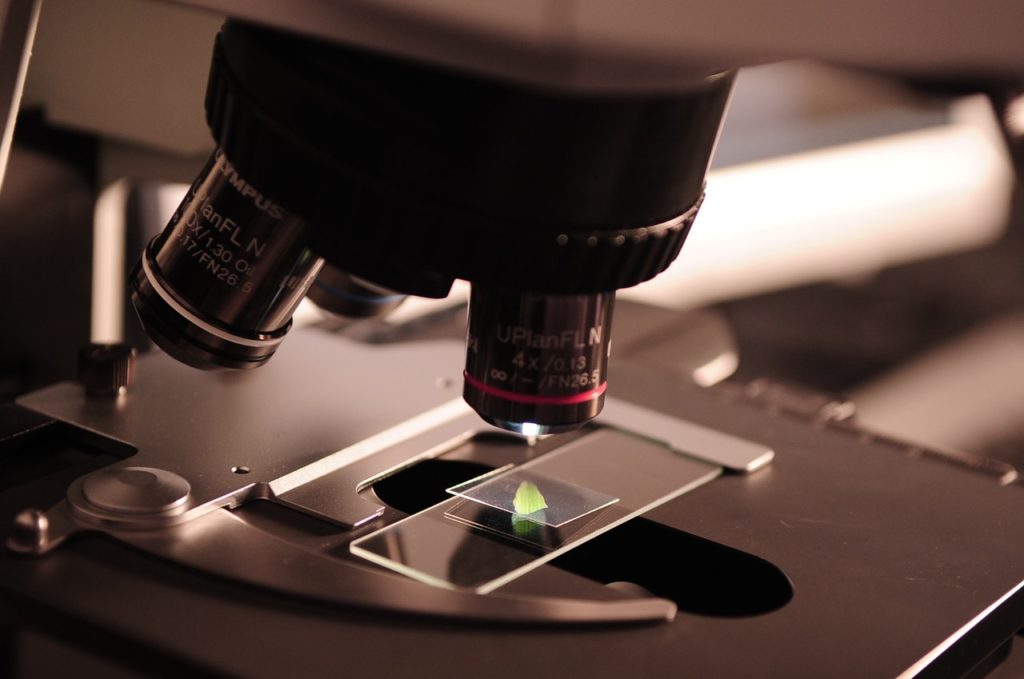

We discussed the base of a microscope above. The area where subjects are placed, usually in slides, is technically referred to as the stage. The stage of a microscope has clips to hold a slide in place and can be adjusted with knobs. The stage also has a small hole called the aperture. This is where light enters the stage and illuminates the subject.
Speaking of the knobs, all microscopes have adjustment knobs used for focus, manipulating the subject, and changing the level of magnification. The focus knobs are usually separated between two types: coarse and fine. Coarse adjustment knobs make big changes, fine adjustment knobs make minor changes. They are useful for getting your subject into the perfect amount of focus so that you can see it clearly. Most microscopes also allow the slide to be manipulated with a knob.
Finally, a microscope also has what’s called a diaphragm or iris, which refers to the apparatus which controls the amount of light flowing through the aperture. Sometimes while looking at a subject you may find that there’s too much or too little light. The adjustment knob for the diaphragm will allow you to control the level of illumination.
How to Purchase a Microscope for Amateur Microscopy
As we briefly touched on in our article Mushroom spores and Microscopy Research, the level of magnification for looking at mushrooms under microscope equipment is more or less what determines the price of a microscope. What you don’t want to do—and a mistake many beginners make—is to buy a cheap “novelty” microscope, the kinds that are usually intended for small children. No, as an amateur microscopist, you want a real microscope. But don’t worry, for the value it can bring to your life, a very decent microscope isn’t that expensive.
Plan on paying within the range of $300 – $600 for a decent microscope with an oil immersion lens. With a setup like that, you’ll be able to reach perhaps 1,000 times magnification, which is plenty enough to start studying mushroom spores.
There are many different kinds of lenses which would be suitable, but an oil immersion lens allows more light to pass through the slide, presenting a sometimes significantly cleaner image. Generally speaking, the more light the better you’ll be able to see your spores.
It’s actually quite possible to get a fantastic microscope in the aforementioned price range. In most cases, and especially as a beginner, you’ll want to avoid purchasing a new device. This is because schools and corporate labs often upgrade their equipment on a regular basis since they really do need the latest and greatest microscopy technology—therefore the second-hand market is often full of excellent microscopes for cheap.
While we wouldn’t say that the second-hand market is flooded necessarily, it’s more than likely that with a bit of searching you should be able to find a very good microscope. Try checking online classifieds and auction websites for the widest assortment and make your purchase from a reputable mushroom spore vendor.
Additional Supplies You May Find Useful for Using A Microscope To Study Mushrooms
In addition to your microscope and high quality mushroom spores, there are a few supplies you may want to keep on hand including:
- Additional slides
- Coverslips to protect your equipment
- Extra microscopic illuminator bulbs
While it’s possible that your microscope came packaged with slides, this isn’t always the case—inquire with your vendor if they include slides, and if not, it can’t hurt to ask them to throw in a few. Otherwise, buy them separately. A package of 25-50 slides should only cost around $10 – $20.

Coverslips aren’t an absolute necessity when you’re starting out, though luckily, these may again be included with your microscope. The main purpose of a cover will be to protect your investment, as the optical components of a microscope can be quite delicate. Any dirt, dust, or grime will also impede the viewing process. While you’re thinking about cleaning, pick up a box of disposable lens tissue paper, which is a specially formulated microfiber tissue designed to clean microscope lenses.
Additional bulbs can be handy to keep around, because in the event a bulb goes out while you’re studying, your research will be stopped in its tracks. Make sure you’re getting the right kind of bulbs for your model of microscope.
You will also want to make sure that you have a special kind of slide called a stage micrometer. This will help you calibrate your microscope, which we’ll discuss in the following section.
Finally, if you went with our recommendation and bought a microscope with an immersion oil lens, you’ll want to get a small supply of immersion oil. Oil immersion works like this: you immerse your lens into the oil as well as your specimen. Since immersion oil has a very high refractive index—how much light it “bounces back” at the viewer—this will increase the available amount of light and thus clarity of the subject.
How to View and Study Mushroom Spores Under Your Microscope
When you buy mushroom spore syringes online, you’ll receive a kit that includes the syringe filled with 10ml of your chosen strain and a sterile needle. The spores are suspended in a non-nutrient liquid, usually distilled water. To view your spores under a microscope, you’ll simply place a single drop or two onto a slide.
Once your specimen is prepared, the next step will be to calibrate your microscope. You’ll notice what looks like a little ruler in the eyepiece. This needs to be compared with your stage micrometer slide (mentioned in the previous section). Mushroom spores are measured in microns. Therefore, you’ll want to calibrate your microscope to view microns. Follow the included instructions with your micrometer slide.
Once you have your specimen prepared and your microscope calibrated, you’ll be ready to start delving into the wonderfully fascinating world of mushroom spores!
Which Mushroom Spores are Best For a Beginner?
Popular mushroom spores for beginners include the:
No matter which mushroom spore you choose, you’re sure to have a wonderful time observing them under your microscope—they’re all beautiful in their own way.
Understanding the Legality of Mushroom Spores in the United States
As you likely already know, mushrooms are illegal in the United States and many other countries. Since spores do not contain any psychoactive substances (unlike mature mushrooms such as cubensis) they are legal to have in most states for research purposes only.
Please always make sure to follow your local laws and learn about the different types of fungi mushrooms.
When in doubt about the main types of fungi mushrooms, do your due diligence and check with reputable mushroom fungi sources.
If you’re excited to start your mushroom fungi or amateur microscopy journey, please feel confident purchasing premium mushroom spores from Qualityspores.store online store. We stock only the highest quality spores and the most interesting strains to study.
